Here are some key points about the kelvin:
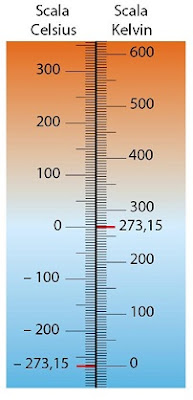
Definition: The kelvin is defined based on the properties of ideal gases. One kelvin is equal to 1/273.15 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water, which is approximately 0.01 degrees Celsius or about 32.02 degrees Fahrenheit.
Absolute Temperature Scale: The kelvin is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it starts from absolute zero, the point at which particles have minimum thermal motion. Absolute zero in the Kelvin scale is 0 K, and no temperature can be lower than this point.
SI Unit: The kelvin is one of the seven SI base units, which serve as the foundation for measuring various physical quantities. It is widely used in scientific and engineering applications, especially in the fields of physics, chemistry, and thermodynamics.
Temperature Conversions: To convert temperatures from degrees Celsius (°C) to kelvin (K), you add 273.15 to the Celsius value: K = °C + 273.15. This conversion is often used in scientific calculations and measurements.
Thermodynamic Scale: The kelvin is part of the thermodynamic temperature scale, which provides a consistent and coherent measurement of temperature, crucial for various scientific and engineering endeavours.
Understanding temperature in kelvin is vital in many scientific disciplines, ranging from fundamental physics to everyday applications. It provides a standardized and universally accepted way to quantify thermal properties and behaviours of substances.

No comments:
Post a Comment